Hazard datasets (WIP)#
Caution
Work in progress page!
Climate-related hazards have traditionally been prominently featured in the conceptualization of climate risk, often dominating the discourse. In this context, the IPCC Assessment Reports (ARs) have played a key role in shaping the role of hazard in climate risk conceptualization, as it is essential for understanding the potential intensity, frequency, and spatial distribution of climate risk.
This page collects references to open-access datasets that characterize climate hazards for the past, present and future. The collected entries are broadly categorized into general datasets that characterize the state of the earth system and datasets created to quantify specific hazards. The collection is not complete and favours datasets with global or European coverage.
Tip
We highly recommend to consider alternative and complementary local datasets for a risk analysis in addition to the options listed here. Contact to your local meteorological service and search for other providers of data tailored to your area of interest. Look out especially for regional climate model projections and statistically downscaled and bias-corrected datasets that take into account local conditions. Some information may only be accessible in the local language.
General climate datasets#
These are datasets of quantities that characterize the Earth system in general. For use a meaningful hazard indicator, they usually require further processing. Available variables include atmospheric temperature, wind speed and precipitation but also information about the state of other Earth system components, e.g., soil properties.
Observations#
Observations comprise information from surface weather stations and other platforms that monitor the state of the Earth system like aircraft and satellites. Consistent and quality-controlled timeseries of observations can be a source of reliable and accurate local information. Some stations have long historical records suitable for analysis of the local climate of the past. However, differences in measurement techniques and equipment can complicate comparisons between observational records in time and space. The spatial and temporal coverage of station data is often incomplete and highly local events, e.g., precipitation extremes, may be missed by the network. Satellites cover large areas in general but only pass infrequently over a specific area if placed in a polar orbit. Gridded observation datasets aim to fill gaps in the coverage by combining observations from different sources with interpolation and statistical techniques.
E-OBS
Daily gridded observational dataset for precipitation, temperature, sea level pressure, relative humidity, wind speed and global radiation in Europe based on ECA&D information.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1950 to near-present
- Spatial coverage
25°N-71.5°N, 25°W-45°E
- Resolution
0.1° and 0.25° horizontal
CHIRPS
Rainfall Estimates from Rain Gauge and Satellite Observations.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1981 to near-present
- Spatial coverage
50°S-50°N
- Resolution
0.05° horizontal
Landsat C2L1
A product from the Landsat missions of Earth observation satellites. Collection 2 is a major reprocessing effort of the Landsat archive, with calibrated multispectral images provided as Level-1 data. Spectral band coverage changes with sensors on newer satellites.
- Dataset
USGS product page and EarthExplorer
- Temporal coverage
Landsat 1 launched in 1972; newest OLI and TIRS sensors on Landsat 8 and 9 since Februrary 2013
- Spatial coverage
global, completed about every 18 days
Reanalysis#
Reanalysis products are recreations of the state of the Earth system by a computer model under the consideration of available observations. Reanalysis datasets provide complete and consistent gridded information in time and space and can be considered a best model estimate for the state of the atmosphere and related components. The approach presents a generally better way to consolidate the information of a diverse and incomplete set of observations when compared to interpolation techniques but limitations of both the model that produces the reanalysis and the coverage of the observational record apply. Notably, reanalysis data is not bound to reproduce the observations and values on the grid usually represent the average conditions in the associated grid boxes. Modern reanalysis products offer explicit uncertainty estimates from an associated ensemble system.
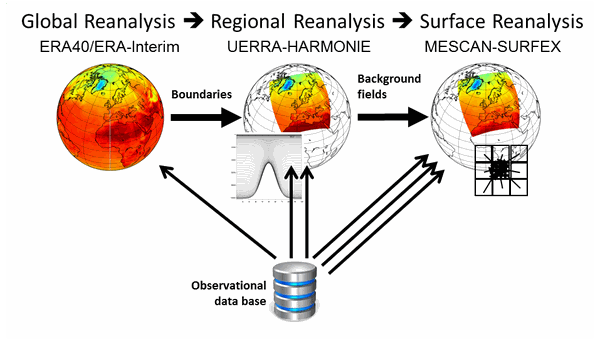
Fig. 13 A global reanalysis provides the boundary conditions for a regional reanalysis, which in turn provides the background for a specialized surface reanalysis. As the modelling of local conditions improves with increasingly specialized models, more observations can be considered in a given area. Source: UERRA data user guide.#
ERA5
Atmospheric reanalysis dataset produced by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), widely used in climate research, weather forecasting, and other applications. Includes an ensemble component at half the resolution to provide information on synoptic uncertainty.
- Dataset
hourly data on single levels, hourly data on pressure levels
- Temporal coverage
1940 to near-present
- Spatial coverage
global
- Resolution
0.25° horizontal
- In workflows
ERA5-Land
ERA5-Land has enhanced horizontal resolution compared to ERA5, but only covers land areas. ERA5-land parameter uncertainty currently can be accessed using the equivalent ERA5 fields.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1950 to near-present
- Spatial coverage
global
- Resolution
0.1° horizontal
CERRA
The Copernicus European Regional ReAnalysis. Inputs are the observational data, lateral boundary conditions from ERA5 global reanalysis and physiographic datasets describing surface characteristics.
- Dataset
single levels, pressure levels, height levels and land component
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
1984 to 2022
- Spatial coverage
Europe, parts of the North Atlantic and North Africa
- Resolution
5.5 km horizontal
UERRA-HARMONIE & MESCAN-SURFEX
Regional reanalysis for Europe produced by the Uncertainties in Ensembles of Regional ReAnalyses project.
- Dataset
single levels, pressure levels, height levels and soil levels
- Temporal coverage
January 1961 to July 2019
- Spatial coverage
Europe
- Resolution
11 km (UERRA-HARMONIE) and 5.5 km (MESCAN-SURFEX) horizontal
Climate model projections#
These datasets are produced by simulations of the Earth system with climate models (“model runs”). As for reanalysis (Fig. 13), there are global climate models (GCMs) and regional climate models (RCMs), with the latter driven by boundary conditions from the former. Climate model runs are usually started in the past and provide a consistent dataset of the historical and future climate. This allows for the correction of model bias with respect to other historical data records and for the assessment of change signals without the introduction of model bias. Projections of climate models depend on assumptions about drivers of the Earth system, which are formalized in emissions scenarios and socioeconomic pathways.
Climate models represent physical processes in varying degrees of simplification. This reduces computational costs but limits how well these processes and their effects are (re)produced in simulations. E.g., many clouds and orographic effects occur at spatial and temporal scales not explicitly resolved by current climate models. Because each model has its specific representation of the Earth system, projections differ between models for the same scenarios. Chaos and stochasticity in the Earth system additionally mean that multiple runs with the same model and scenario do not produce identical projections. Single- and multi-model ensembles of projections should therefore be considered to account for the inherent uncertainties of climate modelling in quantitative CRA.
CMIP6
Global climate model simulations produced for phase 6 of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP). Daily and monthly projections of the historical and future climate from a large number of experiments and models under different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1850-2014 (historical), 2015-2100 (future)
- Scenarios
SSP1-1.9, SSP1-2.6, SSP4-3.4, SSP5-3.4OS, SSP2-4.5, SSP4-6.0, SSP3-7.0, SSP5-8.5
- Spatial coverage
global
- Resolution
depending on model
CMIP5
Global climate model simulations produced for phase 5 of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP). Daily and monthly projections of the historical and future climate from a large number of experiments and models under different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1850 to 2300 (depending on experiment)
- Scenarios
RCP 2.6, 4.5, 6.0, 8.5
- Spatial coverage
global
- Resolution
0.125° to 5° horizontal (depending on model)
CORDEX
High-resolution regional climate model simulations for Europe, produced by a consortium of European research institutions within the Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment. Boundary conditions for the regional climate models come from global climate models of CMIP5.
- Dataset
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
1951-2005 (historical), 1989-2008 (evaluation), 2006-2100 (future)
- Scenarios
RCP 2.6, 4.5, 8.5 (depending on domain and model)
- Spatial coverage
- Resolution
0.11° to 0.44° horizontal (depending on domain and model)
- In workflows
 Extreme precipitation,
Extreme precipitation,
 Urban heatwaves,
Urban heatwaves,
 Agricultural drought,
Agricultural drought,
 Heavy snowfall & blizzards
Heavy snowfall & blizzards
ISIMIP3b
The Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP) provides bias-corrected CMIP6 atmospheric climate data. The bias-adjustment corrects the simulated data towards corrected ERA5 reanalysis (W5E5).
- Dataset
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
1601-1849 (pre-industrial), 1850-2014 (historical), 2015-2100 (future)
- Scenarios
SSP1-RCP2.6, SSP3-RCP7.0, SSP5-RCP8.5
- Spatial coverage
global
- In workflows
ECLIPS-2.0
Bias-corrected and downscaled data of five EURO-CORDEX regional climate models and two greenhouse gas concentration scenarios. 80 annual, seasonal and monthly climate variables for two past and five future periods.
- Dataset
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
1961-1990, 1991-2010, 2011-2020, 2021-2140, 2041-2060, 2061-2080, 2081-2100
- Scenarios
RCP 4.5, 8.5
- Spatial coverage
EURO-CORDEX domain
- Resolution
30 arcsec horizontal
- In workflows
CHELSA-EUR11
Downscaled climate model output of temperature and precipitation estimates from the Climatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas (CHELSA) dataset.
- Dataset
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
1981-2000, 1981-2005, 2021-2040, 2041-2060, 2051-2080, 2061-2080
- Scenarios
RCP 4.5, 8.5
- Spatial coverage
EURO-CORDEX domain
- Resolution
30 arcsec horizontal
- In workflows
Hazard-specific datasets#
They usually built on top of general climate datasets and have additional processing and filtering applied to quantify specific hazards more directly. This ranges from the detection of hazardous events and basic statistical summaries of climate variables in an easy-to-access format to the application of dedicated hazard models to produce hazard indicators.
 Floods#
Floods#
JRC river flood hazard maps for Europe and the Mediterranean Basin region
Gridded inundation depth (in m) along the river network, for nine different flood return periods (from 1-in-10-years to 1-in-500-years).
- Dataset
http://data.europa.eu/89h/1d128b6c-a4ee-4858-9e34-6210707f3c81
- Spatial coverage
Most of geographical Europe and all the river basins entering the Mediterranean and Black Seas in the Caucasus, Middle East and Northern Africa countries. River basins > 150 km².
- In workflows
JRC global river flood hazard maps
Gridded inundation depth (in m) along the river network, for seven different flood return periods (from 1-in-10-years to 1-in-500-years).
- Dataset
- Spatial coverage
Global, except Greenland and Antarctica and small islands with river basins smaller than 500 km²
- Resolution
90 m (3 arcseconds)
WRI Aqueduct Floods Hazard Maps
- Dataset
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
2010, 2030, 2050, 2080
- Scenarios
RCP4.5/SSP2, RCP8.5/SSP2, RCP8.5/SSP3
- Spatial coverage
global
- Resolution
30’’ x 30’’ horizontal
- In workflows
Deltares Global Flood Maps
Inundation maps of flood depth.
- Dataset
https://planetarycomputer.microsoft.com/dataset/deltares-floods
- Spatial coverage
global
- In workflows
Global sea level change indicators from 1950 to 2050 derived from reanalysis and high resolution CMIP6 climate projections
Statistical indicators of tides, storm surges and sea level that can be used to characterize global sea level in present-day conditions and also to assess changes under climate change.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1950 to 2050
- Scenarios
SSP5-8.5
- Spatial coverage
global
- In workflows
IPCC 6th Assessment Report Sea Level Projections
Sea-level projections associated with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Sixth Assessment Report.
- Dataset
- Spatial coverage
global
- In workflows
 Heatwaves#
Heatwaves#
Heat waves and cold spells in Europe derived from climate projections
Number of hot and cold spell days using different European-wide and national/regional definitions developed within the C3S European Health service.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1986 to 2085
- Spatial coverage
European region (approx. 27°N–72°N and 22°W–45°E)
- Resolution
0.1° x 0.1° regular latitude-longitude grid
- In workflows
Online Global Land Surface Temperature Estimation from Landsat
Temperature of the Earth’s surface (as it would feel to the touch), estimated from a combination of Landsat images from different spectral bands.
- Dataset
- Documentation
- Temporal coverage
past; depending on satellite
- Spatial coverage
global, completed about every 18 days
- In workflows
 Fire#
Fire#
Fire danger indicators for Europe from 1970 to 2098 derived from climate projections
Projections of fire danger indicators for Europe based upon the Canadian Fire Weather Index System (FWI) under future climate conditions
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1970 to 2098
- Spatial coverage
Europe
- Spatial resolution
0.11° x 0.11° horizontal
- In workflows
30-Year Canadian Fire Weather Index Simulations over Europe: CMIP6-Informed Temperature and Precipitation Perturbations
30-year Canadian Fire Weather Index (FWI), generated using the Global ECMWF Fire Forecast model, forced by ERA5 reanalysis data (1981-2010). Simulations incorporate perturbations in temperature and precipitation forcings based on CMIP6 climate projections under the SSP2-4.5 medium mitigation scenario.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1981 to 2010
- Spatial coverage
Europe (geographical)
- Resolution
31 km horizontal
 Wind#
Wind#
Winter windstorm indicators for Europe from 1979 to 2021 derived from reanalysis
Climatological indicators on European winter windstorms and their economic impact derived from ERA5 reanalysis.
- Dataset
- Temporal coverage
1979 to 2021; October to March
- Spatial coverage
20°W-35°E, 35°N-70°N
- Resolution
1 km horizontal
- In workflows
